Scrap catalytic converter is one of the most valuable car parts for recycling today. Every modern car uses a catalytic converter to reduce harmful gases from its exhaust. When the converter stops working or the car reaches the end of its life, this part still holds great value.
Scrap Catalytic Converter
Inside, it contains rare metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals are extremely expensive and difficult to find naturally. Therefore, many recyclers focus on collecting and processing scrap catalytic converters. Recycling helps the environment and, at the same time, offers significant financial rewards.
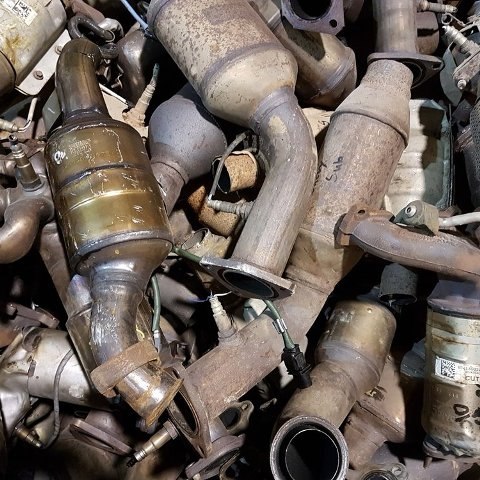

What Is a Scrap Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is a small but powerful device that cleans car emissions. It turns toxic gases into less harmful substances before they leave the vehicle’s exhaust system. When the converter wears out or fails, mechanics replace it. The old one then becomes a scrap catalytic converter.
Even though it no longer works, it still contains valuable metals inside a ceramic honeycomb structure. The honeycomb is coated with a thin layer of platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals allow the converter to perform its function efficiently. Moreover, they make it highly valuable when recycled.
Why Scrap Catalytic Converters Are Valuable
Scrap catalytic converters are valuable mainly because of their metal content. Platinum, palladium, and rhodium are rare and expensive. In fact, mining them requires a lot of energy and causes environmental damage. Recycling, on the other hand, uses less energy and protects nature.
In addition, even a small catalytic converter can contain several grams of these metals. Those few grams can be worth hundreds of dollars. Consequently, recycling and trading scrap catalytic converters have become profitable industries worldwide.
Furthermore, reusing these metals supports a sustainable economy. It reduces the need for new mining projects and helps preserve natural resources for future generations.
How Recycling Works
Recycling a scrap catalytic converter follows several clear steps. Each step helps recover as much metal as possible.
- Collection:
Recyclers gather converters from garages, scrapyards, and car owners. Afterward, they sort them by type, brand, and condition. - Cutting Open:
Next, workers carefully cut open the steel shell to reach the ceramic core inside. They use special tools to ensure safety and efficiency. - Grinding:
Then, the ceramic core is ground into fine powder. This makes it easier to analyze and process later. - Testing:
After grinding, laboratories test the powder to measure how much platinum, palladium, and rhodium it contains. - Melting and Refining:
The powder is then melted in a furnace. As a result, the metals separate from the ceramic material and become pure. - Reuse:
Finally, these recovered metals are used to make new catalytic converters, electronics, and industrial tools.
This process uses far less energy than mining. Moreover, it reduces waste and limits harmful emissions, making it both eco-friendly and cost-effective.
Environmental Benefits
Recycling scrap catalytic converters offers several environmental benefits. First, it reduces the need for new metal mining, which often damages land and uses large amounts of fuel. By recycling, we save energy and prevent soil and water pollution.
Second, it keeps waste out of landfills. Used converters take a long time to break down and can release harmful substances. However, when recycled, they are safely processed and reused.
Furthermore, recycling helps lower greenhouse gas emissions. It is one of the most effective ways to support a greener planet. As a result, every recycled converter helps create a cleaner, more sustainable environment.
Market Demand and Value
The market for scrap catalytic converters continues to grow rapidly. Industries across the world need platinum, palladium, and rhodium for various products. These metals are used not only in catalytic converters but also in electronics, jewelry, and chemical industries.
Prices for these metals often change with global demand. When the price of rhodium or palladium rises, the value of scrap converters also increases. Therefore, traders closely watch market trends before selling.
Moreover, recycling has become an international business. Countries like the United States, Japan, Germany, and South Africa lead in converter recycling. At the same time, many developing nations collect and export scrap converters to refineries abroad. Consequently, the industry supports thousands of jobs and helps drive economic growth.
How to Identify Valuable Scrap Converters
Not all catalytic converters have the same value. However, knowing what to look for can help recyclers earn more profit.
- Vehicle Type: Diesel engines usually contain more platinum, while petrol engines have more palladium.
- Brand: Original manufacturer converters are often worth more than cheaper aftermarket types.
- Condition: Clean, complete converters with intact cores sell at higher prices.
- Serial Numbers: Many recyclers check serial numbers in databases to estimate value accurately.
In addition, keeping detailed records of converter types and conditions helps recyclers make smarter selling decisions.
Economic Opportunities
The scrap catalytic converter industry creates many opportunities. Local collectors, small scrapyards, and large refineries all benefit from this growing market.
For example, small collectors earn money by buying and selling used converters. Meanwhile, large companies refine the metals and sell them to manufacturers. This system ensures that valuable materials never go to waste.
Moreover, governments in several countries now support recycling programs. These programs promote eco-friendly business practices and job creation. As a result, the industry continues to expand and remains profitable year after year.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recycling scrap catalytic converters is both an environmental and economic success. Each converter holds valuable metals that can be recovered, reused, and given new life.
By recycling, we save natural resources, protect the planet, and earn income. Furthermore, this process shows that sustainability and profitability can go hand in hand.
Therefore, whether you collect, trade, or refine, investing in scrap catalytic converters is a wise and responsible choice. Every converter recycled brings us one step closer to a cleaner world and a stronger, more sustainable economy.